Hybrid Laminates PCB
Hybrid laminates PCB (Printed Circuit Board) refers to a type of PCB that utilizes a combination of different laminate materials in its construction. Generally traditional PCBs are typically made of a single material, such as FR-4 (a flame-resistant fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate). However, hybrid laminates PCBs incorporate multiple materials, each with its unique properties, to enhance specific aspects of the circuit board’s performance.
The hybrid laminates PCB technology allows designers to optimize the board’s characteristics for various requirements, such as improved signal integrity, thermal management, mechanical strength, or impedance control. By strategically combining different laminate materials, manufacturers can achieve a balance between these factors, resulting in a more robust and efficient PCB.
Commonly Used Laminate Materials for Hybrid PCB
Some commonly used laminate materials in hybrid laminates PCB include:
- FR-4: FR-4 is a widely used laminate material known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and cost-effectiveness, even more it provides good mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
- Rogers: Rogers laminates are engineered for high-frequency applications, offering low dielectric loss, tight dielectric constant control, and excellent signal integrity. So these laminates are ideal for RF (Radio Frequency) and microwave circuits.
- Metal Core: Metal core laminates feature a layer of metal, typically aluminum or copper, sandwiched between insulating layers. Therefore, the design improves heat dissipation, making it suitable for applications requiring efficient thermal management, such as power electronics and LED lighting.
- Polyimide: Polyimide laminates offer exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and flexibility. As known, they are commonly used in flexible PCBs and applications that require resistance to high temperatures or harsh environments.
- Ceramic: Ceramic laminates provide excellent thermal conductivity, high mechanical strength, and low dielectric loss. They are often utilized in high-power and high-temperature applications, such as power modules and automotive electronics.
By combining these different laminates, hybrid laminates PCBs can be customized to meet specific performance requirements, ensuring optimal functionality, reliability, and durability in various electronic devices and systems.
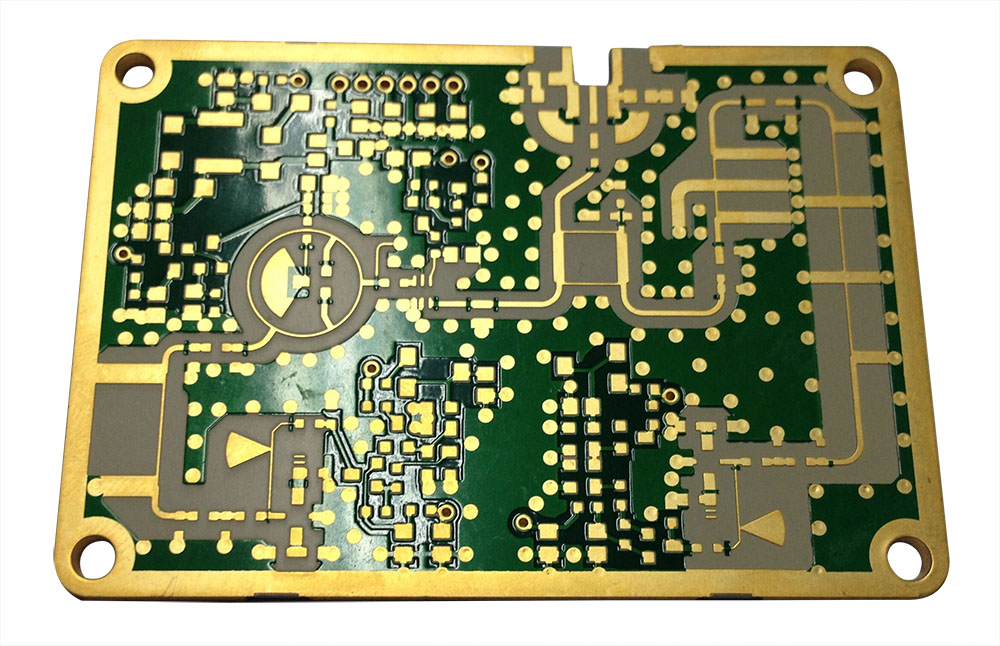
Layers: 4L
Thickness: 1.6mm
Min Hole Size: 0.15mm
Min Line Width: 0.1mm
Copper Thickness: 1oz
Surface Finishing: ENIG
Molding Tolerance:+/-0.05mm
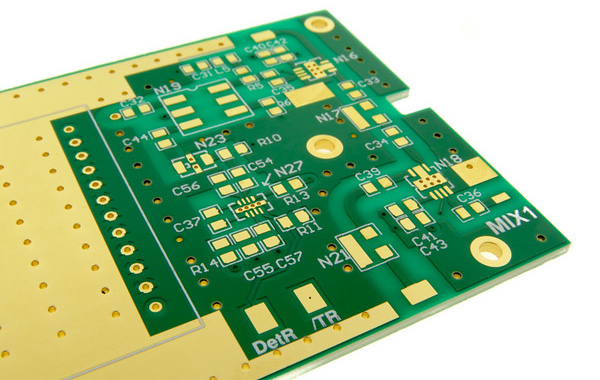
Layers: 4L
Thickness: 1.2mm
Min Hole Size: 0.15mm
Min Line Width: 0.15mm
Copper Thickness: 1oz
Surface Finishing: ENIG
Molding Tolerance:+/-0.05mm
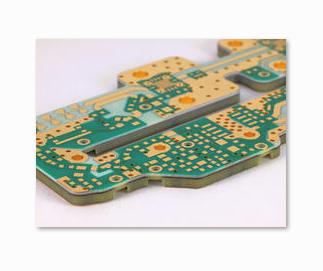
Layers: 4L
Thickness: 1.6mm
Max Length: 1265mm
Min Line Width: 0.1mm
Copper Thickness: 1oz
Surface Finishing: ENIG
Molding Tolerance:+/-0.05mm
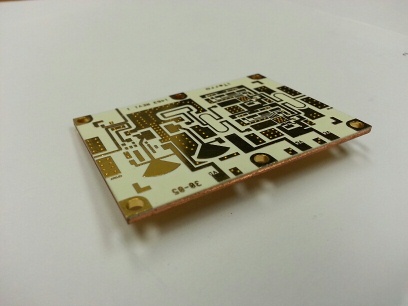
Layers: 4L
Thickness: 1.8mm
Min Hole Size: 0.15mm
Min Line Width: 0.1mm
Copper Thickness: 1oz
Surface Finishing: ENIG
Molding Tolerance: +/-0.05mm